Describe the Process of Bone Formation
Mesenchymal cells condense and differentiate. A Osteocytes deposit calcium and other mineral salts that harden the forming bone matrix.
Bone Formation Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification.

. Parts of the skeleton form during the first few weeks after conception. Process of formation of bone tissue along with the deposition of calcium in the fetal hyaline cartilage is known as ossification. By this process the bones that are located in.
Ossification begins about the third month of fetal life in humans and is completed by late adolescence. Intramembranous ossification forms flat and irregular bones. Secondary ossification occurs after birth and forms the epiphyses of long bones and the extremities of irregular and flat bones.
In humans the process of bone formation begins during 6-8 weeks of embryonic development 1. Ossification begins about the third month of fetal life in humans and is completed by late adolescence. This process occurs primarily in the bones of the skull.
Bone Development Growth. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation called proliferation maturation of matrix and mineralization. It is the form of ossification where there is.
Proper formation of bone depends on sources of calcium phosphorous and vitamin D. Be able to describe as well as recognize in microscope sectionsphotos the process of intramembranous bone formation including the process by which cancellous bone is converted into compact bone. By the end of the eighth week after conception the skeletal pattern is formed in cartilage and connective tissue membranes and ossification begins.
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. Describes the process of bone formation. Five steps can summarize intramembranous ossification.
Bone remodeling involves the removal of mineralized bone by osteoclasts followed by the formation of bone matrix through the osteoblasts that subsequently become mineralized. Bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate. B Chondroblasts secrete cartilage that develops in the shape of bones.
Seen here as density. You have 2 metaphyses. Except for flat bones which form on fibrous membranes most bones develop using hyaline cartilage structure as their models Most simply this process of bone formation or ossification involves two major phases.
C Osteoblasts secrete bone matrix and develop into osteocytes. In intramembranous ossification bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue. Bone formation occurs by osteoblasts secreting an organic matrix osteoid and then mineralizing the matrix.
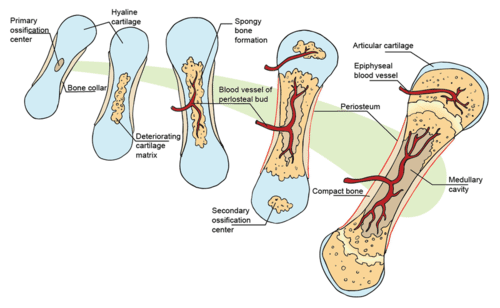
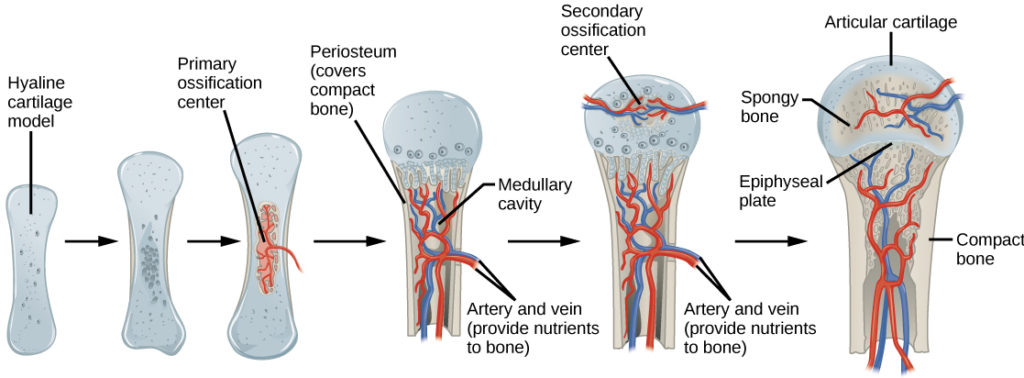
During development these are replaced by bone during the ossification process. First the hyaline cartilage model is completely covered with bone matrix a bone collar by bone-forming cells called osteoblasts. The blastula differentiates into three germ layers.
Osteoblasts osteocytes and osteoclasts. In endochondral ossification bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage. Bone formation also called ossification process by which new bone is produced.
Embryos develop a cartilaginous skeleton and various membranes. The remodeling cycle consists of three consecutive phases. The skeleton is a source of calcium.
All bone formation is a replacement process. Ossification is of two types - A Intramembranous ossification. This problem has been solved.
There are two major modes of bone formation or osteogenesis and both involve the transformation of a preexisting mesenchymal tissue into bone tissue. In intramembranous ossification bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue. Intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification.
In this process mesenchymal. The process takes two general forms one for compact bone which makes up roughly 80 percent of the skeleton and the other for cancellous bone including parts of the skull the shoulder. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation called proliferation maturation of matrix and mineralization.
Calcium phosphate enzyme helps create hard bone from these sources. Bone Formation and Remodelling. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts and group into ossification centers Osteoblasts become entrapped by the osteoid they secrete transforming them to osteocytes Trabecular bone and periosteum form Cortical bone forms superficially. Please update your bookmarks accordingly. In this process the formation of the compact and spongy bone takes place directly from the sheets made of the undifferentiated mesenchymal connective tissue.
Copyright 2008 2005 by Saunders an imprint of Elsevier Inc. The terms osteogenesis and ossification are often used synonymously to indicate the process of bone formation. The skeleton is a metabolically active organ that undergoes continuous remodeling throughout life.
Bone formation also called ossification process by which new bone is produced. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts work to deposit and tear down bone throughout life. Describe the process of bone formation and bone remodeling and repair.
The formation of bone during the fetal stage of development occurs by two processes. We have a new and improved read on this topic. There are two processes of bone formation they are Intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification.
Be able to recognize these cell types. When the remodeling process is aborted say in avascular necrosis bad bone accumulates. In a long bone for example at about 6 to 8 weeks after conception some of the mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes cartilage cells that form the cartilaginous skeletal precursor of.
When the remodeling process is skewed such that over time there is more eating than replenishing you get osteoporosis. Click here to view We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization. First a cartilage model of the bone is formed.
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. Bones at the base of the skull and long bones form via endochondral ossification. Explain what would be the result if there were an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation.
The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis and that of their calcification is termed as ossification. During development tissues are replaced by bone during the ossification process. All bone formation is a replacement process.
The direct conversion of mesenchymal tissue into bone is called intramembranous ossification. All of the following statements accurately describe steps in the process of flat bone formation EXCEPT.

Describe The Process Of Bone Remodeling Orthopaedicsone Clerkship Orthopaedicsone
Growth And Development Of Bones

The Stage Of Endochondral Ossification The Following Stages Are A Download Scientific Diagram

Does Anyone Know About Compact Bone Formation During Endochondral Ossification

Bone Formation Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Endochondral Ossification And Long Bone Growth Beyond Achondroplasia

Osteogenesis Bone Development Intramembranous Ossification Endochondral Ossification Diagram Quizlet

6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy Physiology

Endochondral Ossification An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Seer Training Bone Development Growth

The Stage Of Endochondral Ossification The Following Stages Are A Download Scientific Diagram

6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy Physiology
Growth And Development Of Bones

Endochondral Ossification Youtube
11 5 Bone Growth Remodeling And Repair Human Biology

6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy Physiology

Comments
Post a Comment